Custom Bonded Lenses Standards
Bonded lenses, composed of crown glass and flint glass bonded together, correct the dispersion of glass, eliminating chromatic aberration issues. Dual bonded lenses have found wide applications in multicolor lighting and medical instruments, as well as laser therapy devices. Yibet Optical in Shenyang offers various styles of bonded lenses (achromatic lenses) and provides a range of anti-reflective coating options suitable for ultraviolet, visible, or infrared spectra, including UV-VIS, MgF2, VIS 0°, VIS-NIR, NIR II, or SWIR. Additionally, we offer achromatic lenses specifically designed for ultraviolet or infrared spectra. Compared to standard achromatic lenses with similar wavelengths or comparable wavelength ranges, these custom achromatic lenses offer superior performance.
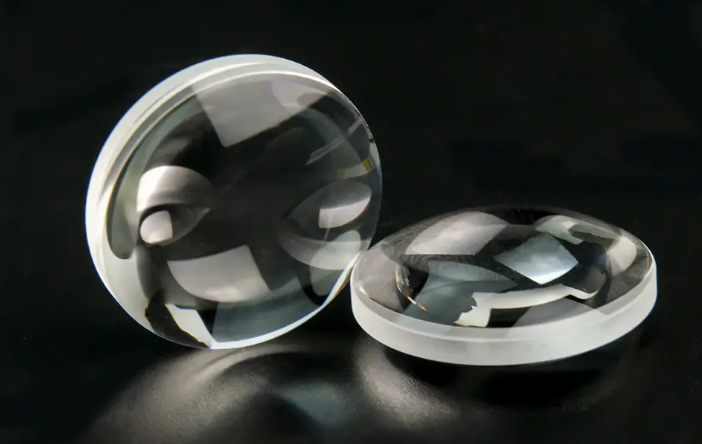

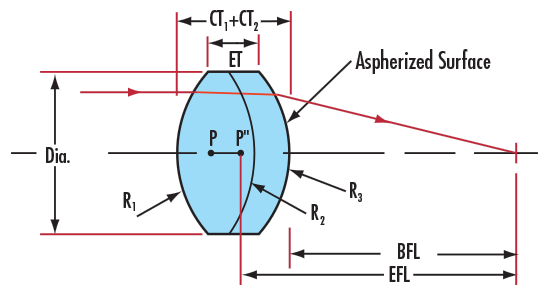
Aspherical achromatic lenses combine the color correction ability of achromatic lenses and the high-quality spherical aberration correction of aspherical lenses, which is also one of the products provided by Yibet Optical in Shenyang. Triple achromatic lenses are suitable for applications requiring a 1:1 conjugate ratio or high-power magnification.
Rigorous size standard controls
- Reduce chromatic aberration
- Custom coating available on request
- Processing parameters for dual bonded lenses
| Diameter Tolerance | 1-600±0.02MM |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Thickenss Tolerance | 0.5-50±0.02MM |
| Surface Flatness | 1/10LAMBDA |
| SufaceQuality | 20-10 |
| Material | N-BK7,FUSED SILICA,SAPPHIRE, CAF2,MGF2,ZNSE |
| Beveling | 45°X0.2MM |
| Coating | Coating Reflective Coating Dichroic Film |
Bonded lenses are used to minimize chromatic aberration to the maximum extent or eliminate it altogether. Their achromatic design also helps minimize spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are suitable for various applications such as fluorescence microscopy, image relays, detection, or spectroscopy. The manufacturing process of achromatic lenses involves bonding two or more elements together. Compared to single lenses, achromatic lenses can produce smaller light spots.